With increasing life expectancy and an evolving financial landscape, retirement planning has become more critical than ever. Yet, many individuals delay saving for retirement due to a variety of reasons – ranging from financial instability to lack of knowledge. According to a 2023 report from the Employee Benefit Research Institute, nearly 30% of Americans aged 45 and older have saved less than $50,000 for retirement, placing them at a significant disadvantage. Starting late can seem daunting, but it is not impossible to build a sufficient nest egg even if you begin in your 40s or 50s. This article explores strategic steps and insights to help you prepare effectively for retirement when you’re starting late.

Assessing Your Current Financial Situation
Before charting out a retirement plan, it is essential to take a clear-eyed look at your current finances. This includes gauging your income, expenses, savings, debts, assets, and projected future cash flows. One practical approach is to compile a detailed monthly budget and identify discretionary spending areas that can be reduced or eliminated.
For instance, John, a 50-year-old graphic designer, discovered that subscriptions and dining out accounted for nearly 15% of his monthly expenses. By cutting these back and redirecting funds toward his retirement account, he raised his savings rate by 10%. Additionally, having a clear understanding of existing debts — such as credit cards, mortgages, or car loans — is crucial because high-interest debt can erode your ability to save efficiently for retirement. Prioritizing debt repayment, especially high-interest debt, can free up funds and reduce financial stress.
One effective method to quantify where you stand financially is to use net worth calculators available online, which consider assets minus liabilities. Moreover, a retirement needs assessment tool can help estimate how much you need to save to support your desired lifestyle upon retirement. Many financial institutions provide free versions of these tools, enabling a data-driven start to your planning.
Maximizing Retirement Contributions and Catch-up Options
When starting late, maximizing your contributions becomes an imperative. The IRS allows for annual contribution limits to retirement accounts such as 401(k)s, Traditional IRAs, and Roth IRAs, which you should exploit to the fullest extent possible.
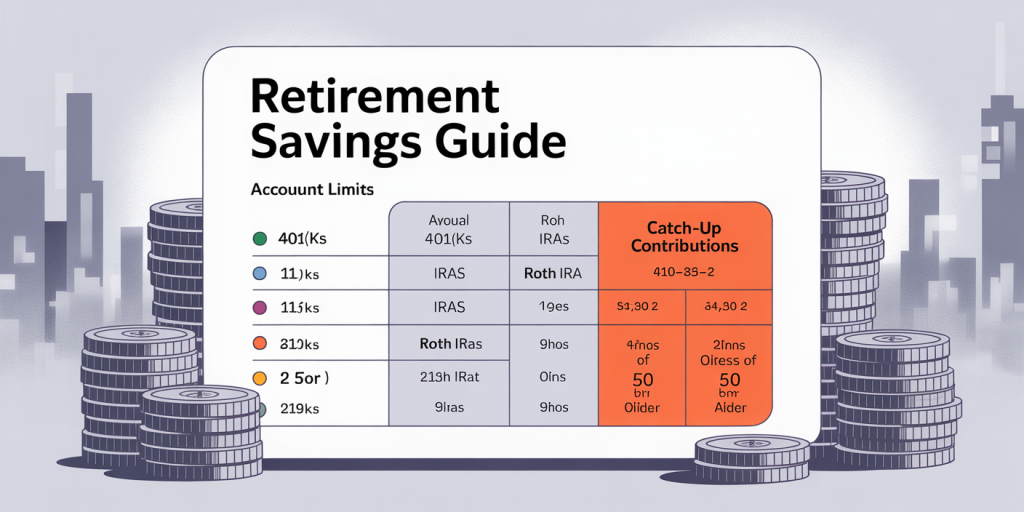
For people aged 50 and older, catch-up contributions provide an excellent opportunity to accelerate savings. For example, in 2024, individuals can contribute up to $22,500 to a 401(k) with an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution, making the total $30,000 per year. Similarly, IRAs allow a standard contribution limit of $6,500, with a $1,000 catch-up contribution for those 50 and older.
To illustrate, consider Maria, who at age 52 realized she had only $80,000 in retirement savings. By increasing her 401(k) contributions to the maximum allowable plus catch-up limits, and investing in a Roth IRA, she was able to boost her retirement nest egg aggressively. This strategy, combined with consistent employer matching programs, accelerated her savings significantly.
| Account Type | Standard Contribution Limit (2024) | Catch-up Contribution Limit (Age 50+) | Total Annual Contribution (Age 50+) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401(k)/403(b) | $22,500 | $7,500 | $30,000 |
| Traditional IRA | $6,500 | $1,000 | $7,500 |
| Roth IRA | $6,500 | $1,000 | $7,500 |
Another tactic is to ensure contributions are made early in the year or even via lump sums during bonuses or tax refunds to take advantage of compounding returns sooner. Even small additional payments towards your retirement account can lead to substantial gains over time.
Diversify Investments and Emphasize Growth Assets
When starting late, your investment strategy must balance risk and time horizon while prioritizing growth to make up for lost time. Generally, younger investors have the luxury to invest more heavily in stocks or stock-focused mutual funds due to their longer timeline to ride out volatility. However, for late starters in their 40s and 50s, a balanced but growth-oriented portfolio often proves prudent.
Scientific studies have consistently shown that equities have historically outperformed bonds with returns averaging roughly 8-10% annually over the last century, compared to 3-5% for bonds. Given a shorter investment horizon, relying too heavily on low-yield bonds could hinder the accumulation of meaningful retirement assets. However, concentration in highly volatile stocks carries risks, especially nearing retirement age. Therefore, diversification is key.
A practical example is a 55-year-old investor named Frank who decided on a 70/30 equity-to-bond split, targeting large-cap stocks, index funds, and dividend-paying stocks for growth, while holding safer bond funds for stability. He rebalanced his portfolio every six months to maintain this allocation. This approach helped him capture growth while limiting downside risk.
Additionally, consider incorporating other investment vehicles such as real estate, REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts), or dividend reinvestment plans which can offer supplemental income or capital growth. As a late starter, leveraging tax-advantaged accounts along with taxable brokerage accounts allows greater flexibility for withdrawal strategies post-retirement.

Control Expenses and Consider Working Longer
When retirement savings lie behind schedule, controlling future expenses and extending your working years can have a substantial impact on your financial readiness. Lowering annual spending requirements reduces the total amount needed in your retirement portfolio, easing pressure on savings.
Many late starters find that postponing retirement by even a few years can compensate for years of limited savings. For example, delaying retirement from 62 to 67 allows additional income accumulation and greater social security benefits. According to the Social Security Administration, the monthly retirement benefit increases approximately 8% annually for each year you defer claiming after full retirement age up to age 70.
To give a real-world application, Karen, a 58-year-old nurse, planned to retire at 62 but after assessing her savings deficit, she extended her career to 65. During this time, she maximized her 401(k) contributions and reduced her household expenses by downsizing to a smaller home. This strategy helped bridge her retirement savings gap while reducing required withdrawals later.
Implementing a frugal mindset and adopting a detailed post-retirement budget can help frame realistic expectations. For example, switching to more cost-effective healthcare options, reducing discretionary travel, or delaying large purchases can conserve financial resources.
Explore Social Security Strategies and Additional Income Streams
Social Security remains a critical pillar of retirement income for many late starters. Understanding the rules surrounding claim age and benefit calculations can optimize the income this benefit provides.
For example, claiming Social Security benefits at age 62 results in a permanently reduced monthly payment compared to waiting until full retirement age (approximately 66-67 years old), whereas deferring claims past full retirement age increases benefits. According to SSA data, a person with a full retirement benefit of $2,000 monthly could see their payment decrease to about $1,500 at 62, or increase to $2,640 if they delay until age 70.
Aside from Social Security, generating supplemental income through part-time work or entrepreneurial pursuits during retirement can be a game-changer. The Gig economy has created flexible opportunities in fields like consulting, tutoring, freelance writing, or driving for ride-share services.
Take the case of Mark, who transitioned into part-time consulting after retiring at 63. His additional earnings not only covered health insurance but also permitted him to maintain a comfortable lifestyle without tapping into his principal retirement savings aggressively.
Carefully factoring in tax implications and withdrawal strategies when combining investment income, Social Security, and work income can optimize your overall financial picture.
Looking Ahead: Preparing for a Secure Retirement Despite a Late Start
Starting retirement planning late does not condemn you to financial insecurity if you commit to proactive and disciplined steps. Adopting a multipronged strategy—evaluating your finances honestly, maximizing contributions, investing wisely for growth, controlling expenses, and leveraging Social Security and work income—can build a meaningful retirement buffer.
As life expectancy continues to rise (the CDC reports an average U.S. life expectancy of 77 years as of 2022, projected to increase), it becomes even more important to plan for potentially 20-30 years of retirement. Advances in healthcare and changing work dynamics offer both challenges and opportunities for late retirement planners. Technologies such as financial apps and robo-advisors enable more personalized and timely investment decisions, while employer-sponsored phased retirement programs provide flexible options.
However, future retirees should also prepare for uncertainties such as inflation, healthcare cost increases, and potential policy changes affecting pensions and Social Security. Regularly revisiting and adjusting your plan is crucial. Collaborating with a certified financial planner can provide customized strategies tailored to your goals, risk tolerance, and timeline.
In summary, starting late means you must embrace frugality, accelerate savings, invest strategically, and plan creatively. While challenging, it is feasible to secure a comfortable retirement with focus and determination. The key lies in taking control immediately, creating a realistic plan, and adapting as your circumstances evolve. With deliberate action, you can still achieve financial independence and peace of mind for your golden years.