Managing personal finances effectively remains a critical concern for millions worldwide. One of the most popular budgeting techniques aimed at controlling spending and increasing savings is the envelope system. Traditionally a physical method involving cash, this system has evolved with digital technology to fit modern lifestyles. This article explores how to use the envelope system both physically and digitally, offering practical insights, comparative analysis, and future perspectives on this timeless budgeting method.
Understanding the Envelope System and Its Relevance Today
The envelope system is a straightforward cash-based budgeting strategy that involves allocating money into separate “envelopes,” each designated for a specific expense category. For instance, you might have envelopes for groceries, transportation, dining out, and entertainment. Once the cash in an envelope is spent, no more money can be used for that category until the next budgeting cycle. This method encourages disciplined spending and helps individuals avoid overspending.
Despite the rise of digital banking and card payments, a significant 62% of Americans report feeling stressed about money, according to a 2023 survey by the American Psychological Association. The envelope system offers tangible control, making money management less abstract. Adopting this method, whether with physical cash or digital tools, can help decrease financial anxiety and boost saving habits.
Setting Up the Physical Envelope System: Step-by-Step
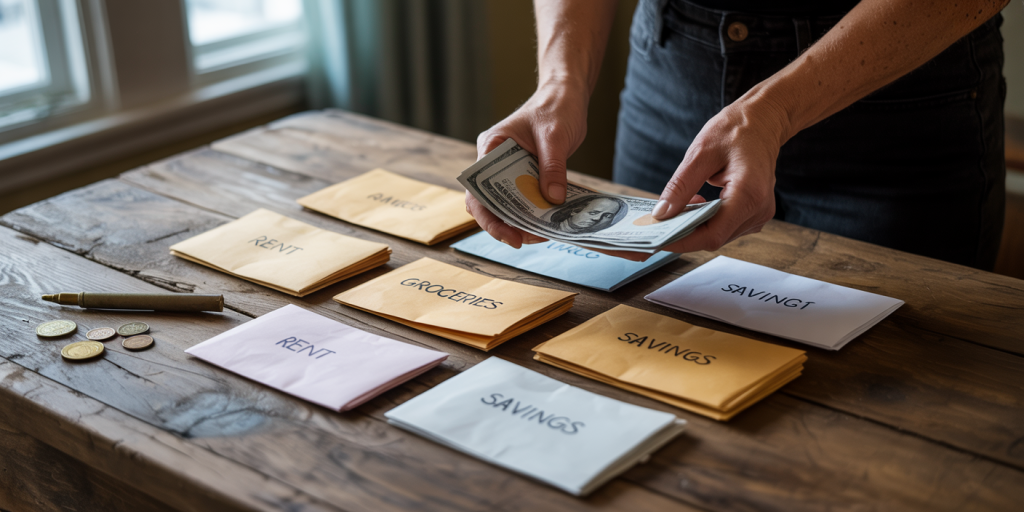
Starting a physical envelope system requires only cash, envelopes, and a clear budget plan. First, determine your total monthly income and subtract necessary fixed expenses like rent, utilities, and loan payments. The remaining disposable income will then be divided into various spending envelopes.
Label each envelope according to spending categories relevant to your lifestyle. For example, a single professional might allocate envelopes for groceries, transportation, eating out, gym membership, and entertainment. A family may include additional envelopes for children’s school supplies, healthcare, and savings.
Once envelopes are labeled, allocate cash to each based on your budget. Suppose you assign $300 to groceries and $150 to dining out. You use cash from these envelopes to pay for expenses. When the cash in the dining out envelope runs out, no more dining out should be done until the next month. To track spending best practices, keep receipts in the envelope.
Many users report a strong psychological effect from using physical envelopes because cash feels more “real” than electronic money. This tactile interaction reinforces self-discipline and makes budgeting more concrete. For example, Jane, a 34-year-old marketing executive, managed to reduce her restaurant spending by 40% within three months of starting the physical envelope system, simply by visualizing and limiting her cash.

Going Digital: Modern Envelope System Adaptations
With the proliferation of mobile banking apps and digital wallets, the envelope system has naturally adapted to the digital age. Financial technology companies such as GoodBudget, Mvelopes, and EveryDollar provide digital envelope systems that mimic the physical method virtually.
To set up a digital envelope system, you begin by linking your bank account to an app and creating virtual envelopes. These apps allow you to allocate funds to each category and track expenses in real-time. Unlike physical envelopes, digital methods enable automated transfers, bill reminders, and detailed analytics to help you get insights into spending trends.
For instance, Sarah, a 28-year-old freelancer, uses every dollar app to allocate her fluctuating income due to irregular freelance projects. Her digital envelope system allows her to adjust her budgets on the go and receive notifications when spending limits are near. This flexibility prevents overspending and helps maintain saving goals, even with variable income.
Digital envelopes offer the added benefit of security, as handling physical cash can result in loss or theft. Additionally, these apps give users the ability to share envelopes among family members or partners to coordinate household budgets efficiently. According to a 2022 FinTech survey, 45% of millennials preferred digital budget tracking apps over physical cash methods, showing the growing trend toward digital finance management.
Comparing Physical and Digital Envelope Systems: Pros and Cons
To better understand which approach suits your lifestyle, consider the following comparison between physical and digital envelope systems:
| Feature | Physical Envelope System | Digital Envelope System |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Cash on hand, immediate use | Online access via phone or computer |
| Tracking and Analytics | Manual, requires receipts | Automated tracking with detailed reports |
| Security | Risk of loss or theft | Password protected, bank-linked security |
| Flexibility | Fixed allocation for the month | Dynamic adjustments based on income/spending |
| Psychological Impact | Tangible cash makes budgeting “real” | Less tactile but convenient and fast |
| Cost | No cost except envelopes | Some apps may charge subscription fees |
| Joint Management | Difficult to share envelopes with others | Easy sharing and syncing with family accounts |
The physical system is advantageous for those who respond well to cash handling, making spending limits more tangible. However, it lacks the functionality of tracking convenience and flexibility offered by digital options.


Conversely, digital envelopes provide seamless syncing with bank accounts and real-time adjustability, appealing to tech-savvy users. Nevertheless, some individuals may find digital budgets less effective psychologically, since digital money can feel intangible and less “real.”
Practical Tips for Maximizing the Envelope System
Regardless of whether you prefer physical or digital envelopes, several effective strategies can enhance the success of your budgeting efforts. First, start by reviewing past spending patterns to create accurate budget categories and allocation amounts. For example, use bank statements or cash receipts from the last three months to understand average spending and unintended leakages.
Second, be consistent with your envelope updates. For physical envelopes, ensure cash is replenished at the beginning of each budgeting period. With digital systems, synchronize your app regularly to maintain accurate spending records.
Third, consider combining both methods if it suits you. For example, some users prefer to keep cash envelopes for variable, discretionary spending categories such as dining out or entertainment but handle fixed bills digitally for convenience and security.
Another useful tip is prioritizing savings envelopes as part of your budget. Even a small amount can accumulate over time. A study by Bankrate in 2023 revealed that 63% of Americans saving consistently attributed their habit to disciplined budgeting systems like envelopes or similar.
Lastly, use the envelope system as a communication tool within families or couples. Set shared financial goals and assign envelopes to joint expenses, teaching fiscal responsibility and transparency.
Future Perspectives: The Evolution of the Envelope System
The envelope system’s future lies in hybrid approaches that combine the psychological benefits of physical cash with the convenience of digital finance tools. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are already being implemented in budgeting apps to provide personalized spending advice and detect financial anomalies.
We also anticipate integration with blockchain technology, enhancing transparency and trust in money management apps. Smart contracts could automatically allocate funds to specific categories on payday or trigger savings transfers based on preset rules, reducing manual budgeting effort.
Moreover, as financial literacy gains importance globally, educational systems are incorporating budgeting exercises modeled on envelope frameworks to teach children practical money skills earlier. According to the Council for Economic Education, youth who learn budgeting methods like envelopes are 30% more likely to maintain long-term savings habits.
With the rise of contactless payments and digital currencies, the envelope system will emphasize behavioral change over merely enforcing cash limits. Virtual reality and gamification may soon make budgeting more engaging, turning money management into interactive experiences.
In summary, whether through tangible cash or cutting-edge apps, the envelope system continues to adapt. Its core principle—allocating limited resources to defined categories—remains a powerful, effective tool for financial discipline in any era.
—
By understanding the mechanics of both physical and digital envelope systems, you can choose the best approach tailored to your lifestyle and financial goals. Employing clear strategies and staying attuned to emerging financial technologies will empower you to control your budget confidently and build a more secure financial future.